Trustless Bridge Architecture (TVM ↔ TVM)
Overview
Trustless bridge is a cross-chain system for token transfers between TVM networks. Unlike relay-based bridge (EVM-TVM), Trustless bridge does not use relay nodes for transfer confirmation. Instead, it uses cryptographic verification via Merkle proofs and LiteClient contracts.
Key Advantage
Users don't need to trust third parties — only cryptography and TVM network validators. This ensures full decentralization of transfers.
Principal Scheme
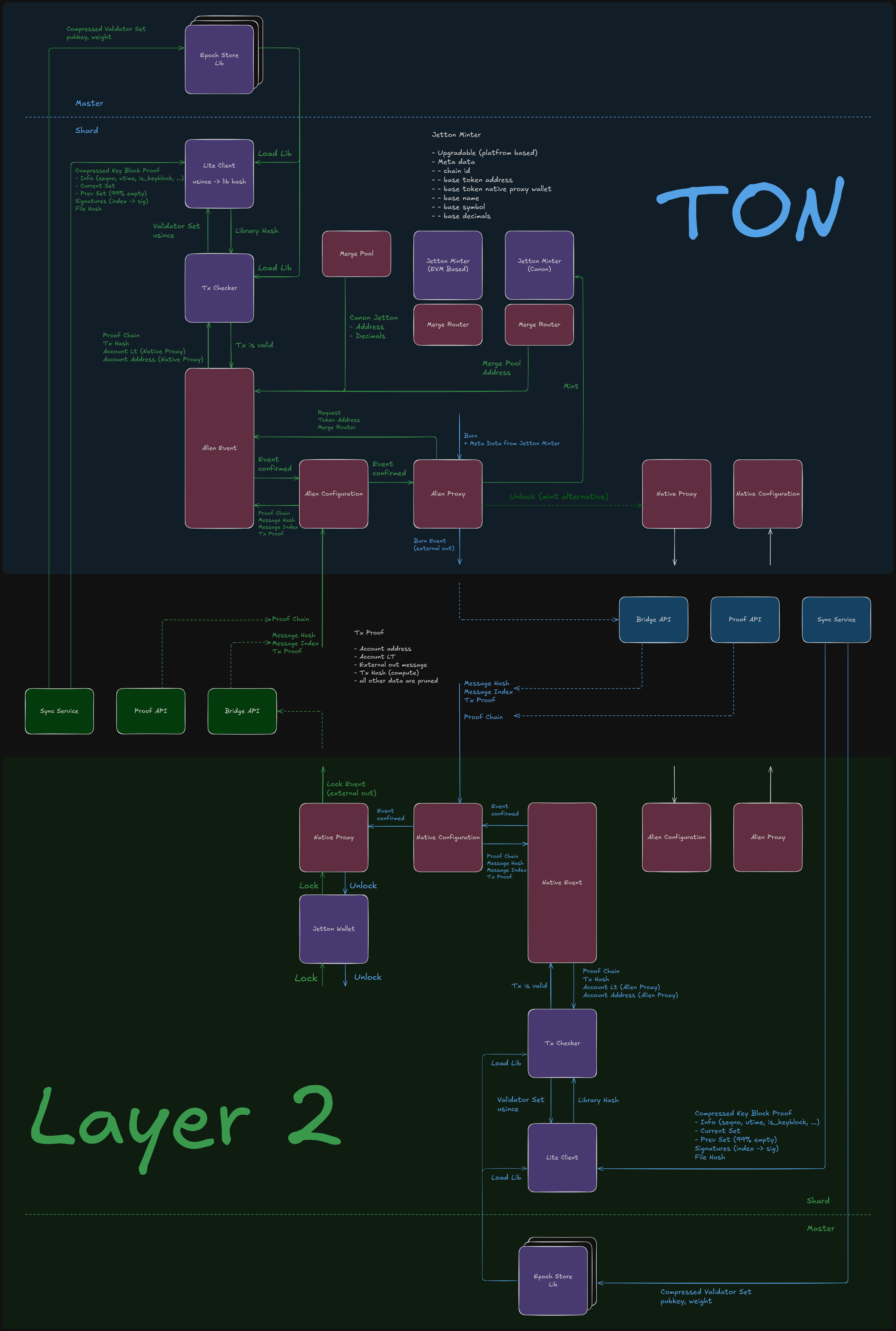
Glossary
Native and Alien Tokens
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Native token | A token that was originally created and exists in this network. When transferred to another network — locked in the Proxy contract. |
| Alien token | A wrapped representation of a token from another network. Created (mint) in the destination network during incoming transfer. Burned during reverse transfer. |
Example:
- USDT on TON network is a Native token for TON
- When transferring USDT from TON to Tycho:
- On TON: USDT is locked in NativeProxy (remains Native)
- On Tetra L2:: USDT is minted (Alien token)
Verification Components
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| LiteClient | Light client smart contract storing information about key blocks of the other network: validator set, their weights, epoch timestamps. Updated by Sync Service during epoch changes. |
| TransactionChecker | Contract for transaction verification via Merkle proofs. Verifies transaction existence in block and block signature validity via LiteClient. |
| Proof Chain | Merkle proofs chain: transaction proof → block proof → validator signature verification via LiteClient. |
| Key Block | TVM network key block containing validator set change information. Synchronized between networks by Sync Service. |
Configuration and Management
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| EventConfiguration | Event configuration contract, manages Event contract deployment, verifies event parameters (chainId, timestamps). |
| NativeProxy | Proxy contract for native tokens. Lock on outgoing, unlock on incoming transfers. |
| AlienProxy | Proxy contract for alien tokens. Mint on incoming, burn on outgoing transfers. |
| MergePool | Contract for consolidating alien tokens from different networks into single representation (canon token). |
| Predeployed Token | Pre-registered token for native-native scenario (token is native in both networks). |
Transfer Types
| Flow | Source Network Action | Destination Network Action | Event Contract |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lock Native → Mint Alien | NativeProxy lock | AlienProxy mint | MultiVaultTvmTvmEventAlien |
| Burn Alien → Unlock Native | AlienProxy burn | NativeProxy unlock | MultiVaultTvmTvmEventNative |
| Lock Native → Unlock Native | NativeProxy lock | AlienProxy → NativeProxy | MultiVaultTvmTvmEventAlien (!) |
Transfer Structure
Important to Understand
Each cross-chain transfer consists of two parts:
- Source network part — locking/burning tokens and emitting an event
- Destination network part — verification and minting/unlocking tokens
Event Contract
For each transfer, a separate Event contract is deployed in the destination network. It performs two key functions:
- Double-spending protection — a contract with a unique address (derived from source message
msgHash) guarantees that one transaction can only be processed once - Participation in Merge logic — the Event contract determines which token the user receives (derive or canon) based on MergePool settings
Verification Mechanism
Overview
Trustless verification is based on three components:
- LiteClient — stores validator set of the other network
- TransactionChecker — verifies transaction Merkle proofs
- Sync Service — synchronizes key blocks between networks
LiteClient and Key Blocks
LiteClient stores information about current validator set of the other TVM network (from which transfers come). This information is updated during validator epoch changes via Sync Service.
Stored data:
current_seq_no— current key block sequence numbercurrent_epoch_since/until— validator epoch start/end timestampscurrent_cutoff_weight— 2/3 + 1 of total validator weightcurrent_validators_set— dictionary: validator_index → (pubkey + weight)
How validator set is updated:
- Sync Service monitors key blocks in source network
- When new key block appears:
- Sync Service downloads block with Merkle proof and signatures
- Calls
new_key_block()on LiteClient
- LiteClient verifies:
- Block Merkle proof is correct
- Block is a key block
- Block signatures are valid for current validator set
- Total weight of signers ≥
cutoff_weight
- Extracts new validator set from block
- Updates stored data
Byzantine Fault Tolerance
Cutoff weight = (total_weight * 2 / 3) + 1 guarantees that signing validator set represents honest majority. Even if up to 1/3 of validators are compromised, they cannot sign an incorrect block.
TransactionChecker and Merkle Proofs
TransactionChecker verifies that transaction exists in block and block is signed by validators (via LiteClient).
Verification algorithm:
- Event contract calls
check_transaction()on TransactionChecker - TransactionChecker decodes proof:
tx_proof— transaction Merkle proofblock_proof— block Merkle proofsignatures— validator signatures
- Verifies transaction presence in block via
lookup_tx_in_block() - Sends
check_block()to LiteClient - LiteClient verifies signatures:
- For each signature checks
check_signature(block_hash, signature, pubkey) - Accumulates
total_signed_weight - Verifies:
total_signed_weight >= cutoff_weight
- For each signature checks
- On success sends
response::transaction_checkedto Event contract
Attack Protection
| Attack | Protection Mechanism |
|---|---|
| Double-spending | Event contract address is deterministically computed from msgHash. Repeat attempt → deployment error |
| Replay attack | EventConfiguration verifies chainId and destinationChainId |
| Forged proofs | Merkle proof is cryptographically verified |
| Invalid signatures | LiteClient verifies total signature weight ≥ 2/3 + 1 |
System Components
On-chain Components (Smart Contracts)
LiteClient
Light client contract storing information about key blocks of the other network.
Stored data:
current_seq_no— current key block sequence numbercurrent_epoch_since/until— validator epoch start/end timestampscurrent_cutoff_weight— minimum signature weight (2/3 + 1 of total validator weight)current_validators_set— validator set with public keys and weights
Operations:
new_key_block— processing new key block, signature verification, validator set updatecheck_block— block signature verification against current validator set
TransactionChecker
Contract for verifying transactions from another network via Merkle proofs.
Operations:
check_transaction— transaction verification:- Extracts transaction and block Merkle proofs
- Verifies that transaction exists in block
- Sends request to LiteClient for block signature verification
- On successful verification sends
response::transaction_checked
ProxyMultiVaultNative (NativeProxy)
Proxy contract for working with native tokens (jettons).
Main functions:
- Receives native tokens (lock) during outgoing transfers
- Sends native tokens (unlock) during incoming transfers
- Emits events for transfers to other networks
- Manages fees and daily limits
Key methods:
transferNotification— callback when receiving jetton tokens, initiates outgoing transferonTvmEventConfirmedExtended— processing confirmed event (completing incoming transfer)
ProxyMultiVaultAlien (AlienProxy)
Proxy contract for working with alien tokens.
Main functions:
- Mints alien tokens during incoming transfers
- Processes callback after burning alien tokens and initiates outgoing transfer
- Manages deployment of new alien tokens
- Works with MergePool/MergeRouter for token consolidation
Key methods:
onTvmEventConfirmedExtended— minting alien tokens during incoming transferonAcceptTokensBurn— callback from jetton contract after token burningdeployTvmAlienToken— deploying new alien token
EventConfiguration (TvmTvmEventConfiguration)
Event configuration contract managing event contract deployment.
Stored data:
- TransactionChecker address
- Event contract code
- Proxy contract address
- Configuration parameters (chainId, startTimestamp, endTimestamp)
Key methods:
deployEvent— deploying new event contract for incoming transfer processingderiveEventAddress— computing deterministic Event contract address frommsgHashonTvmEventConfirmedExtended— callback from Event, proxies call to Proxy
MultiVaultTvmTvmEvent (Alien / Native)
Event contracts for processing specific transfers.
Key methods:
processProof— transaction proof processing, calling TransactionCheckeronTrustlessVerify— callback from TransactionChecker on successful verification_onConfirm— calling proxy to complete transfer
MergePool / MergeRouter
Contracts for consolidating alien tokens from different networks into single representation (canon token).
MergeRouter:
- Routing to corresponding MergePool for token
MergePool:
- Stores derive-token to canon-token mapping
- Conversion between decimals of different representations
Off-chain Components (Backend)
Sync Service
Background service for synchronizing key blocks between networks.
Important
Sync Service runs in background mode and synchronizes key blocks periodically, not for each transfer. This is necessary to maintain current validator set in LiteClient.
Functions:
- Monitors key blocks in source network
- Uploads current validator set information to destination network's LiteClient contract
- Calls
new_key_blockon LiteClient to update validator set
Update frequency:
- Key blocks appear during validator epoch changes
- Usually 1-2 times per day (depends on network)
Proof API
Light node synchronizing blocks and providing API for building proof chain.
Functions:
- Synchronizes all blocks in real-time
- Builds Merkle tree proof for transaction
- Builds block proof
- Endpoint:
GET /v1/proof_chain/{address}/{lt}— returns BOC with proof chain
Bridge API
Event indexer for specific TVM network.
Functions:
- Event indexing from proxy contracts
- Transfer status tracking
- Providing data for event contract deployment
Note: One Bridge API instance serves one TVM network.
Bridge Aggregator API
Aggregator over all APIs for working with transfers.
Functions:
- Preparing payload for transfers
- Combining transfer history from all networks
- Transfer status tracking regardless of networks
Key endpoints:
POST /payload/build— build payload for transfer transactionPOST /transfers/search— search transfers with filteringPOST /transfers/status— get specific transfer status
Event Contract Lifecycle
Event Contract Statuses
| Code | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Initializing | Initial state after deployment |
| 1 | Pending | Awaiting verification via TransactionChecker |
| 2 | Confirmed | Transfer confirmed, proxy called, tokens delivered |
| 3 | Rejected | Transfer rejected (verification failed) |
| 4 | Cancelled | Transfer cancelled by user |
| 5 | LimitReached | Daily limit exceeded, awaiting approval |
| 6 | LiquidityRequested | Liquidity requested from providers |
| 7 | LiquidityProvided | Liquidity provided |
| 8 | Verified | Transaction verified (trustless), but tokens not yet delivered |
State Transition Diagram
Main Flow (Successful Transfer)
- Initializing — EventConfiguration deploys contract, calls
processProof() - Pending — Event sends
verifyTx()to TransactionChecker, awaits response - Verified — TransactionChecker confirmed transaction via
onTrustlessVerify(true) - Confirmed — Event called
_onConfirm(), Proxy executed mint/unlock
Edge Cases
LimitReached (Daily Limit Exceeded)
When transfer amount exceeds daily limit:
- Proxy calls
Event.dailyLimitReached(limitApprover) - Status → LimitReached
limitApprovercan:approveLimit()→ continue transfer → ConfirmedrejectLimit()→ reject → Rejected
- User can:
cancel()→ Cancelled (reverse transfer)
LiquidityRequested (Insufficient Liquidity)
When NativeProxy cannot unlock tokens (insufficient balance):
- NativeProxy calls
Event.notEnoughLiquidity() - Status → LiquidityRequested
- Event requests
eventTokenWalletfor receiving liquidity - Liquidity provider can send tokens with bounty
- After receiving → LiquidityProvided → tokens delivered to user
- Or user can:
cancel()→ Cancelled (reverse transfer)
Bounty for Provider
Liquidity provider receives bounty — reward from user for providing liquidity. Bounty amount is set by user or sender.
Transfer Flows
Lock Native → Mint Alien
This flow describes transferring a native token from source network to destination network where it becomes an alien token.
Step-by-step Description
Step 1-2: Initiation and Locking
User sends jetton tokens to NativeProxy. The payload specifies recipient address and target network. Proxy locks tokens and emits TvmTvmNative event.
Step 3: Event Contract Deployment
Proof API generates transaction Merkle proof. EventConfiguration deploys event contract with proof data in destination network.
Step 4-5: Verification
Event contract calls TransactionChecker for transaction verification. TransactionChecker verifies Merkle proof and requests LiteClient for block signature verification.
Step 6-7: Confirmation
On successful verification, TransactionChecker calls onTrustlessVerify(true) on Event contract. Status changes to Verified. Then Event contract calls _onConfirm(), which:
- Changes status to
Confirmed - Sends
onTvmEventConfirmedExtendedto AlienProxy
Step 8-9: Minting
AlienProxy receives confirmation, checks limits, charges fee and mints alien tokens to recipient.
Burn Alien → Unlock Native
Reverse flow: returning alien token to original network where native tokens are unlocked.
Step-by-step Description
Step 1-2: User burns alien tokens via AlienProxy. Proxy emits TvmTvmAlien event.
Step 3-5: Event contract deployment and verification similar to previous flow.
Step 6-7: Event contract receives confirmation, status changes Verified → Confirmed.
Step 8-9: NativeProxy receives confirmation and unlocks native tokens to recipient.
Edge Case: Insufficient Liquidity
If NativeProxy wallet balance is insufficient for unlock:
- NativeProxy calls
Event.notEnoughLiquidity() - Event → status LiquidityRequested
- Liquidity provider can send tokens with bounty
- Or user can cancel transfer via
cancel()
Lock Native → Unlock Native
Flow for transferring native token between networks where the token is native in both networks.
Implementation Detail
The transfer is technically executed via the Alien flow, but AlienProxy performs a check: if native-native scenario is configured for the token (entry exists in predeployedTokens), AlienProxy doesn't mint the token but proxies the call to NativeProxy.
Step-by-step Description
Step 1-2: User sends native tokens to NativeProxy in source network. Tokens are locked, TvmTvmNative event is emitted.
Step 3-5: In destination network, MultiVaultTvmTvmEventAlien (not Native!) is deployed via AlienEventConfiguration. Verification happens via TransactionChecker.
Step 6-7: Event contract calls receivePredeployedToken on AlienProxy. If token is registered in predeployedTokens, PredeployedTokenData with nativeProxyTokenWallet address is returned.
Step 8-9: After verification, Event contract calls onTvmEventConfirmedExtended on AlienProxy, passing nativeProxyTokenWallet in metadata.
Step 10: AlienProxy checks nativeProxyTokenWallet.hasValue(). If true — doesn't mint, but proxies call to NativeProxy via proxyMultiVaultNative.onTvmEventConfirmedExtended().
Step 11: NativeProxy receives call (accepts from AlienProxy or directly from EventConfig), unlocks native tokens and sends to recipient.
When is this flow used?
Lock Native → Unlock Native is used when token is configured as native in both networks via predeployedTokens in AlienProxy. This is possible for:
- Wrapped native tokens (e.g., wTON)
- Tokens specifically configured by administrator
Configuration happens via registering PredeployedTokenData in tvmConfiguration.predeployedTokens mapping.
Risks and Protection Mechanisms
| Risk | Cause | Protection Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Double-spending | Reprocessing same transaction | Event contract address is deterministically computed from msgHash. Repeat deployment impossible. |
| Forged Merkle proof | Faking transaction proof | Merkle proof is cryptographically verified via extract_merkle_proof() and lookup_tx_in_block() |
| Invalid block signatures | Insufficient signatures or invalid signatures | LiteClient verifies: total signer weight ≥ cutoff_weight (2/3 + 1) |
| Outdated validator set | LiteClient stores outdated validator set | Sync Service periodically updates validator set via new_key_block() |
| Replay attack | Event from one network processed in another | EventConfiguration verifies chainId in proof == networkConfiguration.chainId |
| Wrong destination chain | Event intended for different network | EventConfiguration verifies destinationChainId |
| Unauthorized event emitter | Event emitted not by Proxy contract | EventConfiguration verifies accountAddr == eventEmitter |
| Daily limit exceeded | Transfer amount exceeds daily limit | Proxy checks limits; on exceed → LimitReached status, awaits approval |
| Not enough liquidity | NativeProxy cannot unlock tokens | NativeProxy calls notEnoughLiquidity(); provider can supply liquidity with bounty |
| Wrong predeployed token | Invalid externalNativeProxyWallet | Event verifies match with data from predeployedTokens |
What to do with transfer problems?
- LimitReached — wait for approval from
limitApproveror cancel transfer - LiquidityRequested — wait for liquidity provider or cancel transfer (receive reverse transfer to source network)
- Cancelled — tokens will be returned to source network via reverse transfer
Smart Contract Errors
Event Contracts
Event contract errors (MultiVaultTvmTvmEventAlien, MultiVaultTvmTvmEventNative):
| Code | Condition |
|---|---|
| 2321 | Invalid status for processProof(): status != Initializing && status != Pending && status != Verified |
| 2313 | Call not from EventConfiguration: msg.sender != eventInitData.configuration |
| 2329 | Callback not from TransactionChecker: msg.sender != transactionChecker |
| 2312 | Invalid status for onTrustlessVerify(): status != Pending |
| 2901 | Callback not from Proxy: msg.sender != transitionalData.proxy |
| 2330 | Invalid externalNativeProxyWallet for predeployed token |
| 2326 | Callback not from TokenRoot: msg.sender != transitionalData.token |
| 2327 | Callback not from MergeRouter: msg.sender != transitionalData.router |
| 2328 | Callback not from MergePool: msg.sender != transitionalData.pool |
| 2335 | Call not from limitApprover: msg.sender != limitApprover |
| 2332 | Call not from recipient/sender (for cancel/setBounty) |
| 2324 | Invalid status for operation (approveLimit, rejectLimit, cancel, setBounty, retry) |
| 2333 | Bounty exceeds amount: bounty > eventData.amount |
| 2334 | Callback not from eventTokenWallet: msg.sender != eventTokenWallet |
| 2331 | Callback not from Proxy (Native Event) or not from proxy/native_proxy (Alien Event) |
EventConfiguration
TvmTvmEventConfiguration contract errors:
| Code | Condition |
|---|---|
| 2218 | endTimestamp already set: networkConfiguration.endTimestamp != 0 |
| 2216 | endTimestamp less than startTimestamp |
| 2221 | Proof from different network: chainId != networkConfiguration.chainId |
| 2222 | Invalid msgHash: tvm.hash(message) != _eventVoteData.msgHash |
| 2223 | Event not for target network: destinationChainId != TON_GLOBAL_ID |
| 2220 | Event not from Proxy: accountAddr != eventEmitter.value |
| 2211 | Event before startTimestamp: txTimestamp < networkConfiguration.startTimestamp |
| 2215 | Event after endTimestamp (if endTimestamp != 0) |
| 2212 | Callback not from Event contract: deriveEventAddress(_eventInitData) != msg.sender |
Proxy Contracts
ProxyMultiVaultAlien and ProxyMultiVaultNative contract errors:
| Code | Condition |
|---|---|
| 2710 | Callback not from allowed EventConfiguration: configuration not in tvmConfiguration.incomingConfigurations |
TransactionChecker
TransactionChecker contract errors:
| Code | Condition |
|---|---|
| 200 | Transaction not found in block |
| 201 | Invalid transaction hash |
| 202 | Block is not masterchain block |
| 203 | Callback not from LiteClient: sender_address != ctx_lite_client_addr |
LiteClient
LiteClient contract errors:
| Code | Condition |
|---|---|
| 111 | Block is not key block |
| 112 | Key block from same epoch |
| 113 | Key block from old epoch |
| 114 | Invalid validator signature |
| 115 | Insufficient signature weight: total_signed_weight < ctx_current_cutoff_weight |
| 116 | Invalid validator epoch parameters |
Common Merkle Proof Errors
| Code | Condition |
|---|---|
| 101 | Cell is not exotic cell |
| 102 | Cell is not Merkle proof |
| 103 | Cell is not Merkle update |

